
Publication Review: Raising the Bar for Biomarker Detection in Alzheimer’s Disease
Fast-moving technological advancements are redefining the meaning of ‘good science’. With best practices continuously evolving, it is important to stay up-to-date with the leading tools on the market.
The development of highly sensitive assays and technologies promises new diagnostic value for plasma phosphorylated (P-)Tau levels for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). AD diagnoses have largely relied on information from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to detect levels of key biomarkers such as Tau. However, researchers are looking for less invasive, more accessible alternatives, such as blood plasma.
A recent publication1 by Sherif Bayoumy, Inge Verberk, and their team at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam compares the analytical and clinical performance of several less invasive prototype Simoa® assays and the commercially available P-Tau181 assay from Quanterix.
The Focus on Tau
Tau protein pathology is a key hallmark of AD, but post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation at different sites, produce different isoforms occurring at various stages of disease progression.
Scientists are searching for answers on the best P-Tau isoform to monitor and reliable technologies to non-invasively detect it. By getting clarity on ideal assays, researchers can pursue early detection in cognitively healthy individuals or potentially distinguish between different types of dementia.
A Question of Analytical and Clinical Precision
The researchers set out to answer the question, ‘which of the available P-Tau assays will give researchers the best clinical and analytical outcomes?’
This dual evaluation can inform ongoing studies that use different versions of the available P-Tau assays, and will accelerate the global search for a reliable blood-based biomarker for AD.
The Analytic Approach for Simoa® Assessment
Comparing Cross-Isoform, Multi-Provider Assay Performance
Bayoumy and Verberk’s team performed a direct comparison of 6 P-Tau assays for 3 plasma P-Tau isoforms, from 4 different providers.
The clinical performance was compared using the discriminatory power to differentiate between healthy controls and people with an AD diagnosis. As for the analytical validation, this was the first study of its kind to perform an extensive systematic analytical validation in plasma in one clinical research lab. The researchers measured analytical robustness using various parameters including sensitivity, intra- and inter-assay precision, parallelism, dilution linearity and recovery.
Measuring Assay Performance
Quanterix Demonstrated Precision Robustness
Key Findings at a Glance:
- P-Tau181 Quanterix Simoa® gave precise, reproducible measurements indicative of a stable assay.
- Researchers concluded the P-Tau181 from Quanterix exhibited robust precision, good parallelism, dilution linearity, and recovery.
- Quanterix performed highly for diagnostic accuracy with a good discriminatory potential between AD and controls.
In detail, the P-Tau181 assay from Quanterix demonstrated robust analytical performance, with zero samples with a CV% >20%. Compared to the other assays, it showed good intra- and inter-assay precision, low variability and high specificity and sensitivity.
In terms of clinical performance, all assay results correlated strongly and detected increased P-Tau signals in AD patients compared to controls. The study’s novel assessment of analytical assurance yielded meaningful results from the Quanterix P-Tau181 assay. Taken together, this research highlights P-Tau181 as a sensitive marker for AD pathological changes, and illustrates the value that the Simoa P-tau181 assay can bring to AD research.

Impact on AD Pathology Research
Rigorous testing of products ensures good analytical performance and limits the trial-and-error optimization required at the bench. This allows scientists more time to tackle bigger questions like the best ways to develop routine clinical practices capable of ultra-low biomarker detection.
Dementia is a global epidemic with physical, psychological, social, and economic implications that affect people living with dementia, their families, and society at large. Someone in the world develops dementia every 3 seconds. With an aging population, this problem will continue to grow, putting increased strain on health and social systems.
Early, accurate diagnosis is essential for providing clarity, support, and understanding for people living with dementia. It allows them to safely make important decisions about their future, and aids in their quality of life and mental well-being. The development and commercialization of minimally invasive, ultrasensitive assays will allow for early and safe detection of AD and beyond. Highly sensitive precision tools can help push this scientific possibility closer to reality.
Power Neuropathology Research with Quanterix Simoa® Technologies
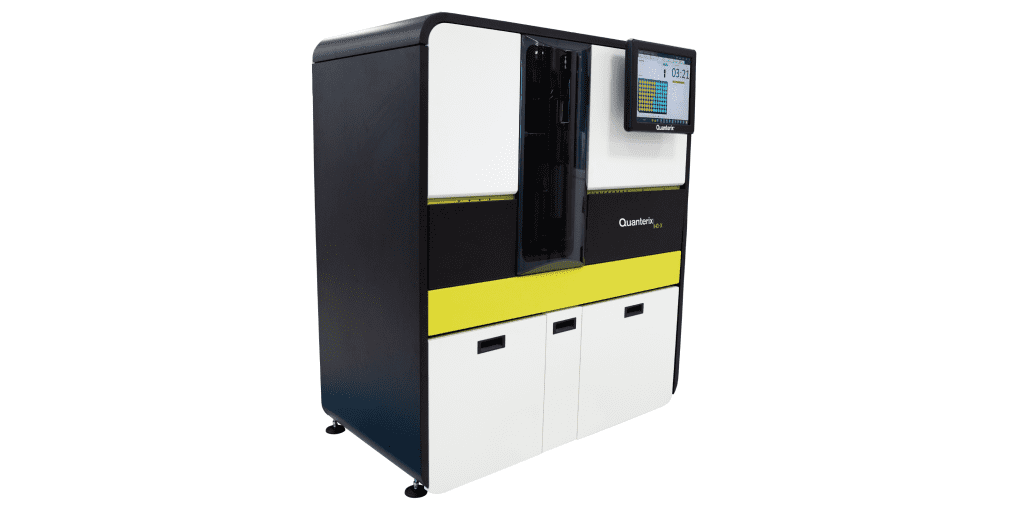
Quanterix Simoa® Technologies is raising the diagnostics bar by providing ultrasensitivity for biomarker detection from plasma.
Analyses performed on the Simoa® HD-X platform can show excellent precision and compatibility with a wide range of custom assays targeting different isoforms from various providers. This makes the HD-X a valuable investment for any neuropathology laboratory looking to further their search for blood biomarkers that aid early diagnosis.
Be at the Forefront of Scientific Discovery
Explore Our Assays for Neurology
References
- Bayoumy, S., Verberk, I.M.W., den Dulk, B. et al. Clinical and analytical comparison of six Simoa assays for plasma P-tau isoforms P-tau181, P-tau217, and P-tau231. Alz Res Therapy 13, 198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-021-00939-9.