
Built for Translation: Why Simoa Stands Alone in Clinical-Grade Biomarker Measurement
Translating proteomic discovery into clinical action requires more than scale, it demands precision, reproducibility, and quantitative clarity. The Quanterix Simoa® digital immunoassay technology, was purpose-built to meet these demands. With attomolar sensitivity, absolute quantitation in pg/mL, and clinically validated deployment across diverse sample types and disease states, Simoa delivers the rigor required for diagnostic confidence.
By contrast, early-discovery platforms such as Alamar’s NULISA-based ARGO HT prioritize multiplex breadth over analytical rigor, often failing to achieve consistent detectability, diagnostic-grade precision, or clinically interpretable quantitation. As head-to-head evaluations confirm, the gap between exploratory tools and translation-grade platforms is not theoretical, it’s measurable. And Simoa is engineered to close that gap.
Workflow Efficiency and Automation – Simoa vs. Alamar
Simoa achieves its ultra-sensitive detection through a streamlined, fully automated immunoassay architecture (Wilson et al., 2016). The HD-X system can process ~1,100 samples per shift with a 4-plex panel, delivering results in ~2.5–4 hours, with minimal hands-on time and consistent throughput.
Alamar’s ARGO HT system, in comparison, relies on NULISA chemistry that incorporates DNA barcoding, multiple bead-capture steps, and a sequencing-based readout. Assay time ranges 7–8 hours, often requiring overnight runs, and throughput is limited to ~288 results per day. While multiplexing is emphasized, automation and ease-of-use are compromised, introducing workflow bottlenecks at precisely the point where clinical operations demand scale and speed.
Analytical Performance: Sensitivity, Precision, and Quantitative Accuracy
Sensitivity and Sample Detectability
In a recent head-to-head evaluation of p-Tau217 assays across eight platforms conducted by Frontage Laboratories, Simoa HD-X was the only platform to achieve 100% detectability in human plasma samples (Zhang et al., 2025). Alamar’s NULISA-based ARGO HT detected only 85%, missing 15% of samples entirely, a significant limitation for any platform intended for use in diagnostic or longitudinal monitoring contexts.
Coefficient of Variation (CV)
Simoa consistently delivers CVs ≤10%, both intra- and inter-assay, a benchmark for clinical-grade reproducibility. Alamar’s platform, however, reported CVs up to 17%, which fall well outside the bounds of diagnostic acceptability and introduce uncertainty into any clinical or translational interpretation.
Absolute vs. Relative Quantitation
Unlike relative quantitation platforms, Simoa reports absolute concentrations in pg/mL. This enables threshold-based diagnostics, cross-study comparability, and precise pharmacodynamic tracking. Alamar reports results in relative NPQ units, which lack standardization and clinical interpretability, undermining their utility in regulated settings.
Clinical Readiness
Simoa assays are validated across numerous disease areas including neurology, immunology, oncology, and infectious disease. In Alzheimer’s research, plasma BDTau and pTau217 measured via Simoa show strong correlation with tau-PET imaging and CSF levels (Palmqvist et al., 2020; Janelidze et al., 2022). In a 13-cohort, multi-center evaluation, Simoa NfL assays delivered inter-lab CVs <10% (Ashton et al., 2021), and in an international round robin proficiency study across 17 clinical sites, the Simoa NfL assay achieved total CV’s <8% across all sites (Wilson et al., 2023). These data highlight cross-site reproducibility essential for trial harmonization.
Simoa also enables homebrew assay development using open protocols and reagents. This flexibility supports rapid deployment of novel biomarkers like pTau205/212. Quanterix maintains a CLIA-certified laboratory generating patient-level reports, and multiple assays are progressing toward FDA IVD clearance, reinforcing the platform’s regulatory maturity.
Real-World Usability
The Simoa platform supports a broad range of validated matrices: plasma, CSF, saliva, urine, and dried blood spots (DBS). This enables deployment in decentralized trials, pediatric populations, and resource-limited settings, a key advantage over platforms like Alamar’s ARGO HT, which are largely limited to plasma and CSF.
With over 2,300 instruments deployed globally, Simoa underpins large-scale biomarker studies, including the DIAN and MS PATHS initiatives. Its reproducibility across laboratories and strong correlation to clinical endpoints make it a reliable translational partner.
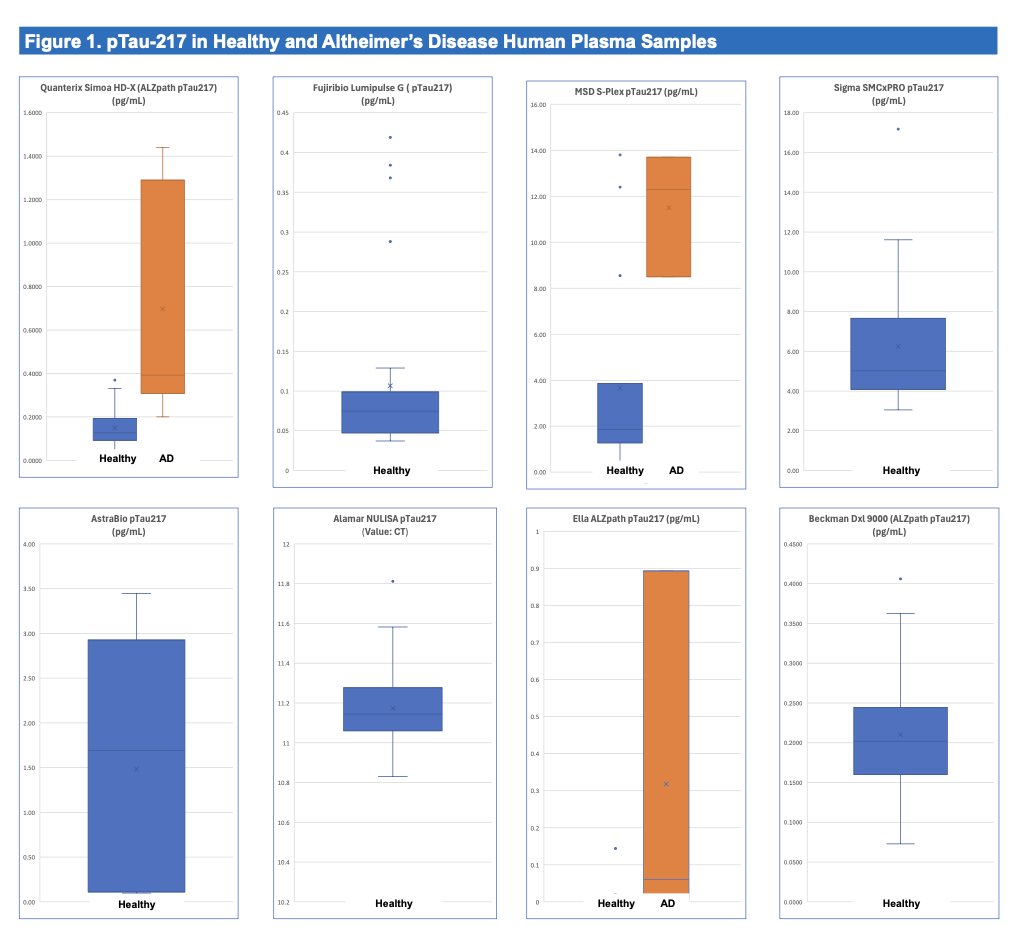
Conclusion: The Data Speaks
The Frontage data leaves little room for ambiguity. Simoa detects 100% of patient samples, delivers <10% CVs, and provides absolute quantitation that supports diagnostics, and regulatory integration. Alamar, by contrast, fails to detect 15% of samples, produces unacceptable variability, and relies on relative units that lack clinical grounding.
As biomarker science moves from discovery into the clinic, platforms must be held to diagnostic standards, not marketing claims. Simoa meets these standards today. It is not simply built for discovery, it is optimized for decision-making.
References:
Ashton, N. J., Janelidze, S., Al Khleifat, A., et al. (2021). A multicentre validation study of the diagnostic value of plasma neurofilament light. Nature Communications, 12, 3400.
Ashton, N. J., Janelidze, S., Al Khleifat, A., et al. (2021). A multicentre validation study of the diagnostic value of plasma neurofilament light. Nature Communications, 12, 3400.
Wilson DH, Rissin DM, Kan CW, et al. (2016). The Simoa HD-1 analyzer: a novel fully automated digital immunoassay analyzer with single-molecule sensitivity and multiplexing. J Lab Autom. 2016;21(4):533-547.
Wilson D., Chan D., Chang L., et al. (2023). Development and multi-center validation of a fully automated digital immunoassay for neurofilament light chain: toward a clinical blood test for neuronal injury. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2023 Sep 13;62(2):322-331.
Zhang, H., Tan, J., Zhang, N., & Lin, Z. J. (2024). Comparison of plasma pTau217 assays on different platforms. The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease, 11(5), 1206–1211.
Written by:
Shana Tetrault, PhD, Director, Product Marketing, Quanterix
David Wilson, VP, Clinical Diagnostics, Quanterix